Welcome to the new era of insurance, where artificial intelligence is fundamentally changing everything from how your policy is priced to how a claim gets handled. Think of AI as a powerful co-pilot for insurers, one that can sift through massive amounts of information to navigate complex risks with incredible precision.
This new capability allows for more personalized premiums, much faster claim processing, and smarter fraud detection. But it all hinges on access to sensitive personal data, which brings up a critical question: how can insurers innovate responsibly while protecting your privacy?
The AI Revolution in Insurance and What it Means for Your Data

The relationship between AI and data privacy in insurance is quickly becoming one of the most important conversations in the industry. Insurers are no longer just passive risk managers; they've become active data analysts, using machine learning to uncover patterns and predict outcomes with an accuracy we’ve never seen before. It’s all part of a bigger industry shift toward more proactive, data-informed operations.
For example, imagine your auto insurer using telematics data, information from a small device in your car, to offer a premium based on how you actually drive, not just on broad demographic averages. Or picture a home insurer using AI to scan satellite imagery after a major storm, allowing them to process thousands of claims almost instantly. These aren't futuristic ideas; they're happening right now.
The Two Sides of the AI Coin
This powerful new tool presents both a massive opportunity and a significant challenge. On one hand, AI promises a more efficient, fair, and customized insurance experience. Policyholders can get coverage that more accurately reflects their individual risk, and claims can be settled in hours instead of weeks.
On the other hand, the fuel for these sophisticated algorithms is your personal information. This goes far beyond just your name and address, potentially including:
Health Records: For underwriting life and health insurance policies.
Driving Behaviour: Monitored through telematics for car insurance.
Social Media Activity: Scanned to spot indicators of potential fraud.
Property Details: Collected from public records and aerial photos.
The core challenge is balancing the immense analytical power of AI with the fundamental right to privacy. Insurers must prove they can be trusted custodians of this data, using it to benefit customers without crossing ethical or legal lines.
This guide will walk you through the real-world applications of AI, the privacy hurdles it creates, the evolving legal landscape, and the best practices for building trust. To get a feel for the wider context of how technology is reshaping the industry, you can learn more about the complete digital transformation in insurance in our detailed article. We’ll demystify this complex topic, providing a clear roadmap for understanding the future of insurance and your data's place within it.
How AI is Reshaping the Insurance Industry

Let's get practical and look at how artificial intelligence is actually changing the insurance business right now. These aren't just futuristic ideas; they're real-world applications that are fundamentally altering everything from how policies are written to how customers are treated.
Every single one of these advancements, however, runs on the same fuel: data. Massive amounts of it. This dependence is exactly why the conversation around AI and data privacy in insurance is so critical. Innovation can't afford to outpace responsibility.
More Precise Underwriting and Risk Assessment
Underwriting used to be a pretty manual, time-consuming job. It relied heavily on generalized statistics and a handful of data points to make big decisions. AI has completely flipped that script, bringing a far more dynamic and precise method to the table.
Instead of just looking at standard details like your age or postal code, AI algorithms can sift through thousands of variables in real time. For example, a property insurer’s AI model can now analyze satellite imagery, historical weather data, local building codes, and even social media trends related to neighbourhood upkeep. This paints an incredibly detailed and personalized risk profile for a single property.
What does this mean for the customer? Fairer, more customized policies. A homeowner who invests in flood barriers or a fire-resistant roof could actually see those proactive steps reflected in their premium; a level of detail old-school models could never handle.
With this granular analysis, risk is no longer a broad estimate. It's a calculated probability, built from a rich, multi-dimensional dataset. Insurance is shifting from being reactive to truly proactive.
Ultimately, this smarter process is a win-win. Insurers can price their risk far more accurately, which reduces their overall exposure. At the same time, customers get rates that genuinely reflect their unique situation.
Faster Claims Processing and Payouts
One of the most noticeable ways AI is making an impact is in claims processing; a part of the business notorious for frustrating delays and mountains of paperwork. AI-powered systems are clearing these bottlenecks at a remarkable pace.
Think about a typical car insurance claim. After a fender-bender, a policyholder can now just snap a few photos of the damage with their phone. AI image recognition software gets to work, analyzing those photos in seconds. It compares the damage against a huge database of repair costs and parts pricing, often generating an estimate and approving the claim almost on the spot.
This kind of automation hits several key targets:
Speed: A process that once took days, or even weeks, of manual inspections can now be done in minutes.
Accuracy: By using data from millions of past claims and removing human subjectivity, the estimates are more consistent and reliable.
Efficiency: This frees up human claims adjusters to apply their expertise to the more complex and severe cases that really need a nuanced, human touch.
Speeding up this process is a massive leap forward for customer satisfaction. It can turn what is normally a stressful ordeal into a surprisingly straightforward experience. To get a better sense of the mechanics, you can see how AI insurance claims processing is a game-changer for the entire sector.
A Better Customer Experience
Finally, AI is also changing the very nature of customer interaction. Insurers are using sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants to offer instant, 24/7 support for routine questions and tasks.
These aren't the clunky, first-generation bots that made you want to pull your hair out. Modern AI assistants can understand natural language, securely access policy details, and handle a whole range of requests, from answering coverage questions to updating personal info or starting a claim.
This gives customers immediate help whenever they need it, while allowing human agents to focus their time on resolving more complicated problems where empathy and critical thinking are essential.
From underwriting to claims to service, each of these applications marks a significant step forward. But their success is directly tied to the quality and quantity of the data they're fed, which brings us right back to the crucial questions of how that information is gathered, used, and, most importantly, protected.
Understanding Key AI Data Privacy Regulations
Trying to navigate the legal side of AI and data privacy in insurance can feel like stepping into a labyrinth. As insurers bring more sophisticated AI tools into their operations, a whole new framework of regulations is popping up to make sure these technologies are used ethically and responsibly. These laws aren't just about dodging hefty fines; they're about building real trust with policyholders who are, understandably, concerned about their data.
At their heart, the principles behind these regulations are pretty straightforward. They're all about giving people more control over their personal information. This means customers have a right to know what data you're collecting, why you need it, and exactly how you plan to use it.
The Cornerstones of Data Protection
Two major pieces of legislation really set the global standard here: the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. While they have their own regional quirks, they both champion the same core idea: empowering the consumer.
For any insurer using AI, these laws create some very specific duties. You can't just hoover up massive amounts of data hoping it might be useful down the road. You have to practice data minimization, which means only collecting the data that is essential for a specific, declared purpose, like calculating a premium or processing a claim.
The visual below breaks down the three fundamental pillars that support any solid data privacy framework.
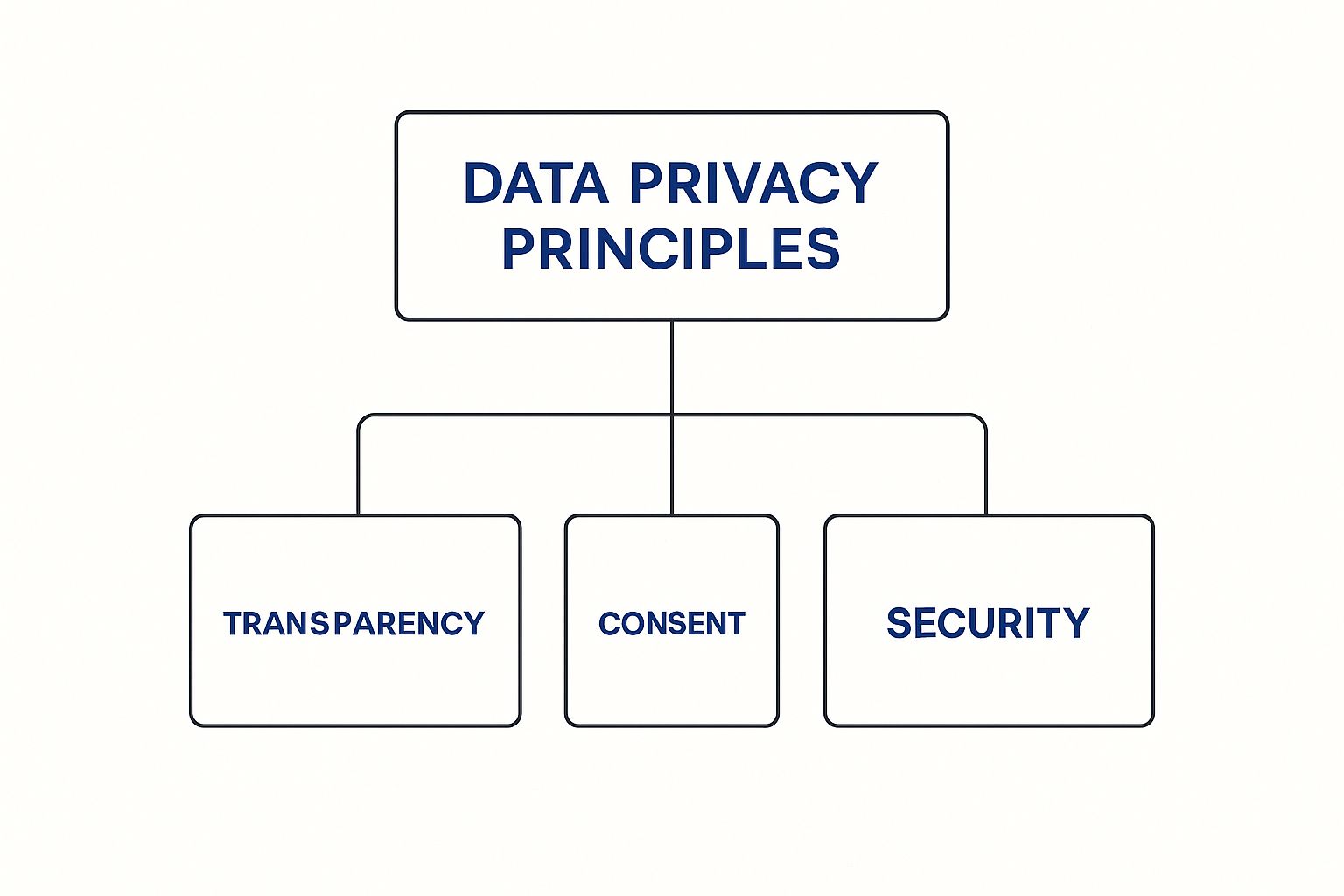
It’s clear that without transparency, consent, and security working in harmony, any data privacy strategy is going to fall short of both regulatory demands and customer expectations.
The Rise of AI-Specific Legislation
As AI becomes more and more common, we're seeing general data privacy laws get updated with rules specifically for artificial intelligence. Regulators are moving fast to tackle the unique challenges that come with automated systems, especially when those systems make big decisions that affect people's lives. This is a critical area to watch in the field of AI and data privacy in insurance.
The following table summarises some of the most important regulations and what they mean for insurers using AI.
Key AI Data Privacy Regulations for Insurers
Regulation | Key Principle | Impact on AI in Insurance |
|---|---|---|
GDPR (EU) | Right to Explanation: Individuals have the right to an explanation for decisions made by automated systems. | Insurers must be able to explain how their AI models arrived at a decision, such as a premium price or claim denial. |
CCPA/CPRA (California) | Right to Opt-Out: Consumers can opt out of the sale or sharing of their personal information and limit the use of sensitive data. | Policyholders can restrict how their data is used in AI-driven marketing or profiling for risk assessment. |
NAIC AI Model Bulletin (US) | Governance & Risk Management: Recommends that insurers develop a formal AI program with clear accountability and risk controls. | Insurers need to establish internal governance structures to oversee the development, testing, and deployment of all AI systems. |
AI Act (EU – Proposed) | Risk-Based Approach: Classifies AI systems by risk level, with “high-risk” applications facing strict requirements. | AI used for underwriting or claims processing will likely be classified as high-risk, requiring rigorous audits and transparency. |
These laws are just the beginning. The regulatory landscape is constantly shifting as technology evolves, so staying informed is absolutely crucial for compliance.
California is really leading the charge here, with its 2025 legislative session zeroing in on AI and consumer protection. Starting January 1, 2025, the state rolled out several AI-specific laws to boost transparency and accountability. A huge change is the regulation of automated decision-making technology (ADMT), which directly impacts how insurers use AI for everything from risk assessment to claims processing. The California Privacy Protection Agency now requires insurers to perform detailed risk assessments for these AI systems. Insurers also have to tell consumers when ADMT is being used and give them a clear path to challenge any AI-driven decision that significantly affects them, like a denied claim or a sudden premium hike.
These new rules give consumers some serious power:
The Right to Know: Insurers have to be upfront about when and how they're using AI.
The Right to Opt-Out: In many cases, customers can refuse to have their data used for certain automated processes.
The Right to Human Review: If an AI makes a big decision, a customer has the right to ask for a person to review the outcome.
To keep up with these complex and evolving rules, many are turning to specialized tools like AI compliance software to help manage the load.
Turning Compliance into a Competitive Edge
Meeting all these regulatory demands might feel like a chore, but it’s actually a massive business opportunity. Insurers who are open and proactive about data privacy are in the best position to earn and keep customer trust. In a crowded market, that trust is becoming a key differentiator.
By treating data privacy as a core business function rather than just a legal hurdle, insurers can build stronger, more loyal customer relationships. It transforms a legal obligation into a powerful statement about the company's values.
Ultimately, the regulations shaping AI and data privacy in insurance are pushing the whole industry toward a more responsible future. They ensure that as technology races ahead, the rights and interests of the individual stay front and centre, creating a safer and more equitable system for everyone.
The Core Data Privacy Risks of Using AI in Insurance

While artificial intelligence can bring incredible efficiency to the insurance industry, it also opens a Pandora's box of serious data privacy and ethical issues. These aren't just minor speed bumps; they're fundamental risks that insurers have to navigate carefully to keep customer trust and stay on the right side of the law.
The concerns around AI and data privacy in insurance are about much more than just keeping data safe. They get to the heart of fairness, transparency, and security, forcing a real rethink of how we handle personal information.
Let's break down the three biggest risks that come with bringing AI into the fold.
The Problem of Algorithmic Bias
Probably the most talked-about risk is algorithmic bias. Here's the thing about AI: it’s only as good as the data you feed it. If an algorithm is trained on historical data that reflects old societal biases, and most historical data does, it will not only learn those biases but can actually make them worse.
Think about an AI underwriting tool trained on decades of claims data. If that old data shows patterns of discrimination against people in certain neighbourhoods, the AI will learn to see those applicants as higher risk, even if it's not true today. It’s not being malicious; it’s just spotting patterns in the data it was given.
This can lead to some pretty serious outcomes:
Unfair Premiums: Certain groups could be systematically charged more for their insurance for reasons that have nothing to do with their individual risk.
Biased Claim Denials: The AI might learn to flag claims from specific communities as more likely to be fraudulent, leading to higher denial rates for them.
Discriminatory Outcomes: At the end of the day, the model could reinforce systemic inequalities, creating huge ethical and legal problems for the insurer.
Algorithmic bias is a quiet but powerful threat. It can create discriminatory outcomes at a massive scale, all while appearing objective on the surface, making it difficult to detect and correct without dedicated oversight.
Regulators are laser-focused on this problem, and they're starting to demand that companies prove their AI systems are fair. It’s on insurers to actively find and fix the bias in their data and models.
The Black Box Dilemma
Another huge concern is what’s known as the "black box" problem. Some of the most sophisticated AI models, particularly deep learning networks, work in ways that are nearly impossible for a human to follow. The model takes in data and spits out an answer, but the complex reasoning it uses to get there can be a complete mystery.
This lack of transparency is a major issue in insurance. If an AI model denies a customer's claim or slaps them with a sky-high premium, that customer and the regulator have a right to know why. "Because the algorithm said so" just doesn't cut it. It shatters trust and makes it impossible to check if the decision was fair, accurate, or even legal.
Amplified Cybersecurity Threats
Finally, the process of building AI systems creates a bigger security target. To train good AI, insurers need to pool together massive amounts of personal data. This creates a treasure trove for cybercriminals.
A single breach of one of these enormous datasets could be devastating, exposing the sensitive information of millions of policyholders. The stakes are incredibly high. A successful attack could compromise everything from health records and financial details to personal driving habits. This makes a rock-solid defence essential. You can learn more about protecting this data in our guide on cybersecurity in the insurance industry.
These challenges are all connected, and they show that you can't just plug in an AI and hope for the best. It requires a thoughtful, responsible approach that puts data privacy and ethics first.
A Framework for Ethical AI and Data Governance
Once you’ve pinpointed the major data privacy risks, it's time to shift from identifying problems to building solutions. A responsible approach to AI and data privacy in insurance isn’t about putting the brakes on innovation. It’s about creating a strong ethical framework and solid data governance to steer it in the right direction. This means getting out of a reactive, compliance-checking mindset and proactively earning customer trust.
The best way to do this is to build privacy directly into your AI systems from the ground up. This idea is known as 'Privacy by Design,' and it basically means treating data protection as a fundamental part of the system’s architecture, not some feature you tack on later.
Adopting Privacy by Design Principles
Putting this proactive mindset into practice means adopting a few key habits that limit data exposure and respect consumer rights from day one. Think of it as installing guardrails before you even start the car; it just makes the whole journey safer for everyone.
These core practices include:
Data Minimization: This is a simple but incredibly powerful rule: only collect, process, and hold onto data that is essential for a specific, legitimate reason. If you don't need a piece of information to accurately price a policy or handle a claim, just don't collect it.
Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Whenever you can, strip out personal identifiers from the datasets you use to train AI models. This lets your algorithms find the patterns they need without tying that data back to a real person, which dramatically lowers the stakes if a data breach ever happens.
When privacy becomes the default setting instead of an afterthought, insurers can build AI systems that are more secure and trustworthy from the start. This creates a sustainable model where innovation and ethical responsibility actually reinforce each other.
Crafting a complete framework for ethical AI and data governance means setting up clear internal rules, like those found in a solid risk management policy template.
The Essential Role of Human Oversight
Technology alone will never be the whole answer. No matter how sophisticated an AI gets, you simply can't overstate the importance of meaningful human oversight, especially when its decisions have a real impact on people’s lives. There must always be a human expert in the loop who has the authority to review, question, and even veto an AI's recommendation.
This becomes absolutely critical in high-stakes moments, like denying a major claim, cancelling someone's policy, or flagging a customer for potential fraud. An algorithm might be great at spotting a statistical outlier, but it has no real-world context or empathy to grasp the full story. A human reviewer provides that crucial check, preventing costly errors and ensuring the process is fair. This "human-in-the-loop" model is really the cornerstone of responsible AI.
This principle doesn't just apply to customers; it's moving into internal operations, too. California’s regulators are now looking at AI systems that affect workforce decisions within insurance companies. Starting October 1, 2025, new employment regulations will kick in to govern automated systems used for hiring and promotions. These rules will require fairness audits and human oversight to combat discrimination, showing just how broad the scope of AI governance is becoming. These strategies aren't just about ticking legal boxes; they’re about building sustainable, trustworthy AI that actually delivers on its promise without sacrificing privacy or ethics.
Your Questions Answered: AI in Insurance
As artificial intelligence weaves its way into the fabric of the insurance industry, it’s completely normal to have questions. For policyholders and professionals alike, the meeting point of AI and data privacy in insurance can seem a bit murky. Let's clear up some of the most common concerns with direct, straightforward answers so you can navigate this new terrain with confidence.
What is the Single Biggest Privacy Risk When Insurers Use AI?
Without a doubt, the biggest risk is algorithmic bias and the discrimination it can cause. It's a common misconception that AI systems are inherently biased. They aren't. The problem is that they learn from the data we give them. If that historical data is laced with decades of hidden societal biases, the AI will not only learn those patterns but can actually make them worse.
Think about it this way: an AI model might notice a correlation between certain postal codes and a higher number of claims. What it doesn't see is the complex socioeconomic reality behind that data. The algorithm, with no human ill intent, could start charging higher premiums to everyone in that area, effectively discriminating against entire communities. It's a sneaky kind of unfairness because it’s hidden inside what looks like an objective, data-driven system.
The real danger here is that AI can rubber-stamp past injustices at an enormous scale, all under the guise of neutral math. This is precisely why things like regular audits, using diverse training data, and keeping a human in the loop aren't just good ideas, they're essential shields against unfair outcomes.
It's also why new regulations are popping up, all aimed at making sure automated decisions are fair and consumers are protected.
How Can I Find Out if My Insurer is Using AI for My Policy?
You absolutely have a right to know. Thanks to modern data privacy laws like GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California, transparency is no longer optional. Insurers have a growing legal duty to tell you when automated decision-making technology (ADMT) plays a major role in decisions that affect you, like setting your premium or deciding on a claim.
So, where do you look? Start with the company's privacy policy or terms of service. You might also get a specific notice when you apply for or renew a policy. These documents should give you a heads-up about how your data is being used by their automated systems.
On top of that, these laws give you some powerful rights:
The right to an explanation: You can ask for a breakdown of the logic behind an automated decision that impacts you.
The right to human review: You can demand that a decision made solely by an algorithm gets a second look from a real person.
If you have a hunch that AI was used to make an unfair decision about your policy, the best first step is to call your insurer. Ask them to walk you through their process and specifically mention your right to have a human review the outcome.
Does Using AI Make My Personal Data Less Secure?
It's not a simple yes or no; it definitely raises the stakes. To learn and function, AI models need to be fed massive amounts of data. This means insurers are creating these huge, centralized pools of incredibly sensitive information, from your health records to your driving habits. Naturally, a treasure trove like that becomes a prime target for cybercriminals. One successful breach could be catastrophic.
But here's the other side of the coin: AI can also be a formidable security guard. In fact, many of the most advanced cybersecurity systems today use AI to spot and shut down threats in real time. These AI tools are fantastic at catching weird patterns that might signal an attack, reacting far faster than any human team could.
Ultimately, it all comes down to the insurer’s priorities. If a company is investing heavily in AI for underwriting but skimping on AI-powered security, then yes, the risk goes up. A balanced approach is the only way to manage this new level of risk effectively.
Will AI Completely Replace Human Insurance Agents?
It’s extremely unlikely. While AI is brilliant at crunching numbers and handling repetitive work, it’s missing the very things that make a great insurance professional: empathy, nuanced ethical judgment, and the ability to have a real conversation. Those skills are, and will likely remain, uniquely human.
What we're really heading towards is a hybrid or collaborative model. Picture AI as a super-powered assistant, working alongside human experts to make them even better at their jobs.
Here’s what that looks like in the real world:
An AI could sift through thousands of data points to give a preliminary risk score for a complicated business policy, but an experienced human underwriter makes the final, critical judgment call.
A chatbot can handle simple questions 24/7, like "When is my payment due?" which frees up human agents to help clients through the stress of a major claim or find the perfect coverage for their family.
This partnership lets the industry get all the speed and efficiency of automation without losing the human touch that builds trust and creates lasting customer relationships.
At Cleffex Digital Ltd, we understand the delicate balance between pushing technology forward and doing it responsibly. We help businesses navigate their digital journey with custom software solutions that prioritize security and user trust. Discover how our expertise can help your business grow.







