Picture having a personal health assistant right in your pocket. Not just something that tracks your steps, but a tool that helps your doctor spot health problems before they become serious. This is the new reality being built with AI-driven healthcare apps, which are making patient care more predictive, personal, and efficient.
Why AI Is Reshaping Healthcare Right Now
AI-driven healthcare apps are smart software programs that use technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to analyse massive amounts of health data. It’s best to think of them less as digital tools and more as active partners in a patient's health journey. They are helping shift healthcare from a reactive model, treating people when they're already sick, to a proactive one focused on keeping them well.
This big change is happening because a few key technologies have all matured at once. First, nearly everyone has a smartphone, and many people use wearables like smartwatches that track heart rate. This creates a constant stream of real-time health data that we’ve never had before. At the same time, cloud computing has given us the raw power needed to process all that information, allowing AI algorithms to find subtle patterns that would be impossible for a human to catch.
Expanding the Possibilities in Patient Care
So, what does this actually look like in a clinic or a hospital? It’s far more than just step counters and calorie logs. These apps are opening up entirely new ways to deliver care:
Early Disease Detection: AI algorithms can scan medical images, like MRIs or photos of a skin lesion, and flag early signs of diseases like cancer or diabetic retinopathy with incredible accuracy.
Personalised Treatment Plans: By looking at a patient's genetic makeup, lifestyle habits, and real-time vital signs, AI can help clinicians craft highly specific treatment plans, finally moving us past the old one-size-fits-all model.
Chronic Disease Management: For someone managing diabetes or high blood pressure, these apps offer constant monitoring, send medication reminders, and provide personalised advice to help them stay on track.
Streamlined Administrative Tasks: For clinic staff, AI is a huge help. It can automate tedious jobs like scheduling appointments or organising patient records, freeing up clinicians to spend more time with their patients and reducing burnout.
This guide cuts through the hype to give clinics, startups, and healthcare leaders a practical roadmap. We’ll dig into how these intelligent tools are changing everything from diagnostic accuracy and patient engagement to the bottom line.
Ultimately, the aim is to build a healthcare system that's more connected and works smarter, not just harder. You'll get the practical steps for developing, launching, and measuring the success of these applications, starting with the foundational ideas that make it all possible.

Exploring the Types of AI-Driven Healthcare Apps
To really get a handle on how AI is changing healthcare, it helps to look at where it’s actually being used. When you break it down, these applications fall into two main camps that cover everything from patient care to the back-office operations that keep a hospital running.
The two big categories are clinical applications, which directly help with diagnosing and treating patients, and non-clinical applications, which are all about making the administrative side of healthcare run a lot smoother. Seeing this distinction is the first step in figuring out where AI can make the biggest difference for your organisation.
Clinical AI Applications
Think of clinical AI applications as a trusted partner for healthcare professionals, helping them make smarter, faster decisions. These tools are designed to sift through mountains of complex medical data and spot patterns that the human eye might miss.
For instance, in medical imaging, AI algorithms can analyse X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to flag subtle abnormalities, like tiny tumours or hairline fractures, often faster and with greater consistency than a human could alone. It doesn't replace the radiologist, but it adds a powerful layer of support to their expertise.
These apps are also a cornerstone of personalised medicine. By looking at a patient's genetics, lifestyle, and medical history all at once, AI can help map out a treatment plan that's truly built for them. We're finally moving past the one-size-fits-all approach and toward care that’s far more effective. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on AI clinical decision support.
AI in a clinical setting is like giving a doctor a set of super-powered glasses. It doesn't replace their expertise but allows them to see patterns and details in patient data that are invisible to the naked eye, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Non-Clinical AI Applications
While the clinical tools often get all the attention, non-clinical AI apps are the unsung heroes working behind the scenes. They’re quietly fixing the logistical headaches and administrative burdens that contribute to delays, rising costs, and clinician burnout.
A huge area here is workflow automation. AI-powered systems can take over tedious but essential jobs like scheduling appointments, managing billing cycles, or even transcribing a doctor's spoken notes into a patient's record. This frees up everyone, from front-desk staff to senior physicians, to focus more on what matters most: the patients.
Another major area is patient engagement beyond the clinic's walls. Take mental wellness apps, for example. Many use AI chatbots to offer 24/7 support, providing coping strategies and a listening ear whenever someone needs it. This space is booming, which tells you just how much people need accessible mental health tools. In Canada alone, the AI-heavy mental health apps market hit USD 305.4 million in 2024 and is expected to climb to USD 716.2 million by 2030, according to research from Grand View Research.
Clinical vs Non-Clinical AI Healthcare Applications
To really nail down the difference, it helps to see these two categories side-by-side. Both are aimed at making healthcare better, but their day-to-day functions, who uses them, and their ultimate goals are quite distinct.
Here's a quick comparison of AI-driven healthcare app categories, showing their function, target user, and a real-world example to illustrate just how broad AI's impact really is.
| Application Category | Primary Function | Example Use Case | Target User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | Diagnosis, treatment, and patient monitoring | An AI algorithm that detects diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans. | Doctors, nurses, radiologists, and other medical specialists. |
| Non-Clinical | Administrative tasks and operational efficiency | An automated system for scheduling patient appointments and managing hospital bed availability. | Hospital administrators, front-desk staff, and patients. |
At the end of the day, you can't have one without the other. Clinical apps push the boundaries of what's possible in patient care, while non-clinical apps build the efficient, reliable system needed to deliver that care effectively.
2. Designing the Architecture for Your AI Healthcare App
Think of building an AI-driven healthcare app like constructing a state-of-the-art hospital. You wouldn't start laying bricks without a detailed blueprint, and in the world of AI, that blueprint is your technical architecture. It’s the invisible framework that makes sure your app is stable, dependable, and genuinely effective. And it all begins with the most fundamental building material: data.
High-quality data isn't just important; it's the absolute foundation of any worthwhile AI model. Without it, even the most advanced algorithm is useless. This means your data has to be diverse, covering a wide spectrum of patient demographics to sidestep biases that could lead to unfair or incorrect health outcomes. It also needs to be rigorously secured and anonymised from the very beginning to protect patient privacy.
The mind map below shows how these architectural pieces fit together for both clinical and non-clinical applications.
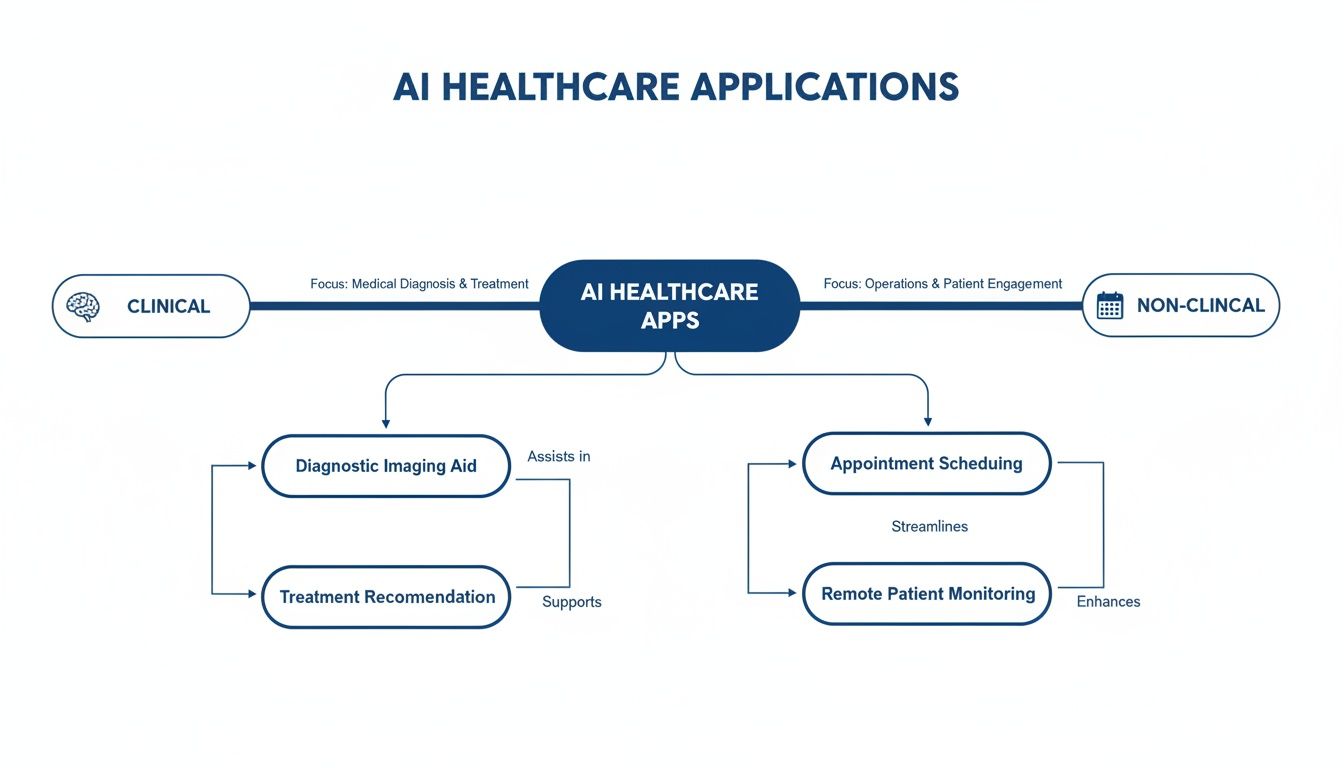
You can clearly see the split between the diagnostic and treatment-focused clinical side and the operational, efficiency-driven non-clinical side. This illustrates the two distinct, yet often connected, paths AI development can follow in healthcare.
Choosing the Right AI Model
With a solid data foundation in place, the next big decision is picking the right AI model for the job. This is like choosing the right medical specialist for a specific condition. There are two main categories to consider, and each has its own unique strengths.
Machine Learning (ML) Models: Think of these as skilled detectives. They excel at sifting through structured data, things like patient records, lab results, and vital signs, to spot patterns and predict outcomes. An ML model, for instance, could analyse a patient's history to forecast their risk of developing a chronic illness.
Deep Learning (DL) Models: These are more like expert radiologists or pathologists who specialise in interpreting complex, unstructured data. As a subset of machine learning, deep learning uses neural networks that mimic how the human brain works. This makes it incredibly powerful for tasks like analysing medical images, whether that's identifying cancerous cells on a pathology slide or spotting subtle anomalies in an MRI.
The choice really comes down to what you want your app to do. If you're predicting patient readmission rates, a machine learning model is your best bet. But if you’re building an app to read and interpret X-rays, you'll need the power of a deep learning model. To create truly effective AI-driven healthcare apps, you first need to understand what an AI native app builder is and how it serves as the ground floor for this kind of modern development.
Ensuring Accuracy and Building Trust
Just building a model isn’t enough. You have to prove it works correctly and, just as importantly, you need clinicians to actually trust its recommendations. This is where model validation and explainability become critical.
Model validation is the demanding, multi-stage testing process that confirms an AI's accuracy and reliability. It involves training the model on one set of data, then testing it on a completely different, unseen dataset to see how well it performs in the wild. This step is absolutely essential for preventing "overfitting" – a common pitfall where a model learns its training data so well that it fails to make accurate predictions on new, real-world information.
After validation comes Explainable AI (XAI), which tackles the "black box" problem. Clinicians are, quite rightly, sceptical of trusting a recommendation if they can't understand how the AI reached its conclusion.
XAI techniques pull back the curtain, showing which specific data points pushed the AI toward its decision. For example, an AI that flags a skin lesion as potentially cancerous might also highlight the exact features, like irregular borders or certain colour variations, that led to its assessment.
This kind of transparency is the bedrock of clinical adoption. It allows doctors to use AI not as an infallible oracle, but as a sophisticated co-pilot that enhances their own expertise. You can get a broader perspective on creating these tools in our guide on healthcare software development.
By designing a thoughtful architecture built on high-quality data, the right models, and a firm commitment to validation and explainability, you can create an app that isn't just technologically impressive but is also worthy of trust in a clinical setting.
4. Navigating Privacy, Security, and Regulatory Compliance
In healthcare, trust isn't a bonus feature; it's the foundation everything is built on. When a patient uses an AI-powered app, they're handing over some of their most personal information. They have to believe, without a shadow of a doubt, that it's being protected.
This is where regulatory compliance becomes non-negotiable. Launching an app without a rock-solid understanding of these rules is like building a hospital without adhering to a single building code. It’s not a matter of if it will fail, but when.
For any app operating in Canada, the starting point is the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA). This is the federal law setting the ground rules for how private companies collect, use, and share personal information. Think of it as the national standard for data privacy.
But it doesn't stop there. Healthcare is often a provincial matter, so you also have to master the local rulebook. In Alberta, for instance, the Health Information Act (HIA) lays out very specific requirements for handling health data. These laws aren't just obstacles to clear; they’re the very blueprint for earning and keeping user trust.
Adopting a Compliant-by-Design Mentality
To get this right, you have to bake compliance into your app from the very beginning. This “compliant-by-design” approach means privacy and security are core design principles, not just items on a pre-launch checklist. It’s the difference between slapping a padlock on a finished door and engineering a bank vault from the ground up.
So, what does this look like in practice? It means implementing a few critical technical safeguards from day one:
End-to-End Encryption: All data must be scrambled and unreadable to anyone without authorisation, whether it's sitting on a server or moving between the app and the cloud.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): A password alone is no longer enough. MFA adds that essential second layer of security to confirm a user's identity before they can access anything sensitive.
Secure Data Handling Protocols: You need strict internal policies that dictate who can access data, how it’s managed, and when it should be anonymised. Only the right people should be able to interact with it, under the right conditions.
When you build compliance in from the start, you're doing more than just avoiding fines. You're sending a powerful message to patients and providers that you take their privacy seriously. That’s how you become a solution they can truly depend on.
Practical Steps for Ensuring Compliance
Knowing the rules is one thing, but putting them into action is what counts. Before you even think about deploying a new healthcare app, it's absolutely vital to conduct a thorough Privacy Impact Assessment. This process is designed to help you spot and fix potential privacy risks before they become real problems.
The sheer volume of data in healthcare today makes this more important than ever. Consider an initiative like GEMINI, which pulls 12 billion data points from 35 hospitals in the Toronto area. Managing that kind of data flow securely is a massive challenge. It’s why new, privacy-preserving techniques are emerging to help develop compliant and effective AI models.
To get started, here's a practical checklist to keep your project on the right track:
Get Explicit Consent: Don't bury permissions in fine print. Clearly tell users what data you’re collecting and exactly how you plan to use it. They must actively agree before you process anything.
Practice Data Minimisation: Only collect what you absolutely need for the app to work. Every extra piece of data you gather is another piece you have to protect, which increases your risk.
Create a Clear Data Breach Protocol: Hope for the best, but plan for the worst. You need a detailed, step-by-step plan for what to do if a security breach happens, including how you’ll notify users and regulators.
By weaving these principles into your development process, you can build AI-driven healthcare apps that are not only innovative but also fundamentally trustworthy.
For a deeper dive, check out our post on data privacy for AI in Canadian healthcare.
Integrating AI into Existing Clinical Workflows

Even the most brilliant AI tool is set up to fail if it adds friction to a clinician's already frantic day. The true test for AI-driven healthcare apps isn't just about the power of their algorithms; it’s about becoming a seamless part of the clinical environment. The goal is to design a tool that feels like a trusted partner, not another frustrating hurdle.
This all comes down to interoperability – the ability of different systems to talk to each other and share data. Without it, your app is just an isolated island of information, cut off from the vast ocean of patient data living in the hospital's core systems.
Making AI Speak the Language of Healthcare
Think of it this way: your AI app and the hospital’s Electronic Health Record (EHR) system speak different languages. To have a meaningful conversation, they need a universal translator. In health tech, that's where standards like HL7 and FHIR come in.
HL7 (Health Level Seven) is the long-standing, traditional standard for exchanging clinical and administrative data between different healthcare software.
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is the modern successor. It’s a more flexible, web-friendly standard that makes it far easier for systems, including mobile apps, to exchange information quickly and securely.
By building your app to "speak" FHIR, you ensure it can pull a patient’s history from the EHR and push its own findings back into the official record. This creates a single, unified source of truth for every patient's journey.
Best Practices for a Smooth Rollout
Getting an AI app into the hands of clinicians involves much more than just a technical connection. It demands a thoughtful strategy focused on adoption, trust, and long-term performance. A rushed deployment can easily disrupt workflows and kill any confidence staff might have had in the new technology.
Here are a few key strategies to get it right:
Phased Rollouts: Instead of a "big bang" launch across the entire hospital, start with a pilot program in a single department. This gives you a controlled setting to gather real-world feedback, iron out the kinks, and prove the app's value before scaling up.
Practical Training: Forget feature-heavy slide decks. Provide hands-on training that shows clinicians exactly how the app solves their specific problems, whether it's saving time on paperwork or flagging at-risk patients sooner.
Build a Feedback Loop: Create a simple, direct channel for users to report issues and suggest improvements. When you act on that feedback, you show clinicians you value their expertise and are committed to making the tool work for them.
The push for this kind of integration is picking up serious momentum. In Ontario, an initiative is aiming to get 10% of primary care clinicians using ambient AI scribes by late 2025, with that number expected to hit 50% by spring 2026. These tools are already slashing documentation time by 70-90%, and with 83% of clinicians wanting to keep using them, the demand is crystal clear. You can read more in this C.D. Howe Institute report.
The best measure of successful integration is invisibility. The AI should feel like a natural part of the workflow, not an extra task to manage.
Finally, long-term success depends on constant vigilance. One of the quietest but most significant challenges is model drift, where an AI's performance slowly degrades as real-world data patterns evolve. You have to keep a close eye on the model's accuracy and retrain it with fresh data. This ongoing monitoring and maintenance ensures the AI remains a reliable and effective clinical partner for years to come.
How to Measure Success and Prove Your ROI
Getting an AI healthcare app up and running is a major milestone, but the real work begins when you have to prove it was worth the effort. It's easy to get caught up in technical wins like model accuracy or how fast it processes data, but what stakeholders really need to see is tangible value. This means shifting the conversation from abstract data science metrics to the concrete clinical and business results that matter to patients and your budget.
You have to move the discussion out of the development lab and into the real world of day-to-day healthcare. Stop asking, "How accurate is the algorithm?" and start asking, "By how much did this app reduce our 30-day readmission rates?" or "How many person-hours did we free up in the billing department last quarter?" This is the kind of outcome-focused thinking that builds a rock-solid business case, secures ongoing funding, and shows everyone the true impact of the technology you’ve built.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators That Matter
If you want to know if your app is a success, you have to decide what "success" looks like before you even launch. That means defining the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from day one. These metrics can't be generic; they must be tied directly to the specific problem you’re trying to solve, whether that’s making your clinical team more efficient or helping patients stick to their treatment plans.
Think about your KPIs in a few different buckets:
Clinical Outcomes: This is the big one. These metrics tell you if you're actually improving patient health. Are you seeing lower hospital readmission rates, fewer post-op infections, or better medication adherence?
Operational Efficiency: This is all about saving time, money, and headaches. You can track things like a drop in administrative workload, a faster patient check-in process, or less time clinicians spend buried in paperwork.
Financial Impact: These are the numbers that connect the app directly to your organisation's bottom line. Measure things like the total cost of care for certain conditions, a reduction in unnecessary tests or procedures, or even an increase in revenue from more efficient billing.
Patient and Staff Satisfaction: A great app shouldn't just be effective; it should make life better for the people using it. Use tools like Net Promoter Score (NPS) to gauge patient satisfaction and keep an eye on metrics related to clinician burnout and job satisfaction.
Calculating a Clear Return on Investment
Your Return on Investment (ROI) calculation is what turns all those KPIs into a compelling financial story. The basic formula is simple: take your financial gains, subtract the project cost, and divide it all by the project cost. But remember, the "gain" isn't always direct revenue. More often than not, it comes from all the money you saved and the efficiencies you created.
Your ROI calculation isn't just a formula; it's the story of your app's value. It should clearly show how an upfront investment in technology resulted in measurable improvements to care quality, operational speed, and financial health.
Take patient engagement apps, for example. They have massive ROI potential. A Phoenix survey highlighted that while only 9% of Canadians turn to AI first for health information, 37% trust its advice for weight loss. Drilling down, 44% trust AI to calculate their daily calorie intake and 41% to create meal plans. You can read more about these Canadian AI health trends on Business Wire. This kind of trust leads to higher patient engagement, which in turn leads to better long-term health outcomes and lower costs for managing chronic diseases.
When you focus on the right metrics, you can confidently shift the conversation from cost to value. You’ll be able to prove that your AI-driven healthcare app isn't just another expense; it's a strategic investment in a healthier, more efficient future for everyone.
Your AI in Healthcare Questions, Answered
Diving into the world of AI-driven healthcare apps can feel overwhelming. Whether you're a provider, developer, or hospital administrator, you likely have a lot of questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to help you get a clearer picture.
What Is the Biggest Challenge in Developing an AI Healthcare App?
Without a doubt, the single biggest hurdle is data. Getting your hands on enough high-quality, properly anonymised data to train a reliable AI model is a massive challenge.
And it’s not just about quantity. The data needs to be diverse and representative of your entire patient population. If it isn't, you risk building algorithmic bias right into your tool, which could lead to skewed or even unfair health outcomes for certain groups. On top of all that, you have to navigate the complex web of data privacy and regulatory compliance, like PIPEDA, which adds another significant layer of difficulty. It’s a problem that demands careful, expert planning from day one.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Compliant Healthcare App?
The timeline really depends on what you're trying to build. For a relatively straightforward Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that meets all compliance standards, you’re probably looking at a timeline of six to nine months.
But if you're aiming for something more sophisticated, like an app with advanced diagnostic AI and deep integrations into hospital Electronic Health Records (EHRs), the project could easily stretch to 12 to 18 months, or even longer. The compliance piece alone adds a lot of time for security audits, detailed documentation, and the rigorous testing needed to guarantee patient safety and protect their data.
It’s crucial to remember that compliance isn't a one-and-done task. Building a trustworthy app means weaving security and privacy into every single stage of development, not just checking a box at the end.
How Can Smaller Clinics Afford to Implement AI Technology?
This is a common concern, but smaller clinics definitely don't have to miss out. The trick is to shift your thinking away from building a custom AI solution from the ground up, which is a very expensive route.
A much more practical approach is to look at existing Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms. Many of these tools are already powered by AI and are designed to solve specific problems, like automating appointment scheduling, streamlining medical billing, or helping with clinical notes. By starting with a focused, subscription-based tool, smaller practices can get the benefits of AI without the massive upfront investment, making it an affordable and effective starting point.
At Cleffex Digital Ltd, we focus on building secure, compliant, and genuinely useful AI-powered healthcare solutions. We know how to handle the complexities of data, compliance, and integration because we do it every day.
Ready to build the future of healthcare? Learn how Cleffex can bring your vision to life.