When it comes to fintech, AI-powered fraud detection isn't a fancy add-on anymore; it's an essential line of defence. It’s about using sophisticated machine learning algorithms to sift through user behaviour and transaction data in real-time, catching complex fraud schemes before they can do any real damage. This is a massive leap from older, rule-based systems and is absolutely vital for protecting a business and its customers today.
The New Frontline in Fintech Security

The fight against financial fraud has evolved. It’s no longer a simple cat-and-mouse game but a full-blown technological arms race. For fintechs, especially the small and medium-sized ones, the stakes are incredibly high. Modern fraudsters are armed with advanced tools to orchestrate complex attacks that can easily bypass traditional security measures.
Think of those old-school fraud systems like security guards with a rigid checklist. They’re good at spotting known offenders, a blacklisted IP address or a name that doesn't match, but they're easily outsmarted by new tricks. They simply don't have the context or the flexibility to see the bigger picture of a coordinated attack as it’s happening.
Why AI Is The Essential Defence
AI, on the other hand, operates like a team of seasoned detectives. Instead of sticking to a fixed set of rules, these systems are constantly learning from fresh data, spotting subtle patterns and unusual connections that scream "fraud." This gives them the power to identify threats that have never been seen before.
This ability to adapt on the fly is what makes AI so critical in fighting modern financial crime. It can flag emerging threats like synthetic identity fraud, where criminals invent entirely new identities, or advanced account takeovers designed to perfectly mimic a real user's behaviour.
This guide will walk you through how AI-powered fraud detection in fintech has become the core defence mechanism for any company looking to survive and grow. As criminals get smarter, you need intelligent systems that can keep up. For a broader look at how this fits into the industry, you might find this overview of automation strategies in financial services quite useful.
AI is already making a huge impact across the board, helping businesses in a few key ways:
Protect Revenue: By catching fraudulent transactions before they go through, companies slash direct financial losses and avoid expensive chargebacks.
Maintain Customer Trust: When customers feel their money and data are safe, they stick around. Strong fraud prevention is the foundation of that trust.
Scale Securely: As a business expands, you can't manually review every transaction. AI automates the grunt work, letting you grow safely without drowning your team.
These proactive defences are fundamental to building a resilient business. To dig deeper into this, you can also explore some effective strategies to enhance fintech app security that work hand-in-hand with an AI-first approach.
How AI Spots the Crooks Hiding in Plain Sight
To really get why AI is such a big deal for fraud detection, you have to forget about the old, rigid rules-based systems. Think of those as a bouncer with a very specific checklist. If a transaction ticks a box on the "known fraud" list, it's blocked. Simple, but easy for clever criminals to sidestep once they figure out the rules.
AI-powered fraud detection is a whole different ball game. It’s less like a bouncer and more like a seasoned detective. Instead of a static checklist, it uses dynamic, learning models to sift through millions of data points in the blink of an eye, looking for subtle clues, context, and weird behaviour that just doesn't feel right.
And the need for this kind of advanced security has never been greater. Fraud losses in Canada have ballooned to a shocking $643 million – almost three times what they were in 2020. That kind of number puts immense pressure on fintech companies, especially smaller businesses that can't afford a massive security team. For a deeper dive into the national response, Canada's new National Anti-Fraud Strategy is a good place to start.
First, You Have to Know What's Normal
The secret sauce behind AI security is something called behavioural analytics. Before an AI can flag a fraudster, it first has to get a crystal-clear picture of what "normal" looks like for every single customer. It quietly observes and learns each person's unique financial fingerprint.
It’s constantly asking questions behind the scenes:
Transaction Times: Does this person usually buy things during the workday or in the middle of the night?
Geographic Locations: Are they typically in Toronto, or are transactions suddenly pinging from three different continents at once?
Device Usage: Is this login coming from their usual iPhone, or is it a brand-new Android device they've never used before?
Purchase Amounts: Is this their regular $5 morning coffee, or a sudden, out-of-the-blue $5,000 purchase?
By building this incredibly detailed profile, the AI creates a baseline for what to expect from each user. It's a living, breathing profile that evolves with every single tap, click, and purchase.
It's a bit like knowing a good friend so well you can tell something's wrong just by the way they text. You might not be able to point to one specific thing, but the combination of their word choice, timing, and what they're asking for just screams "off." AI does the exact same thing with financial data, picking up on tiny deviations from the norm.
The Brains of the Operation: Machine Learning Models
This is where the magic of machine learning (ML) really kicks in. We train these ML algorithms on massive datasets filled with both legitimate and fraudulent transactions. Over time, the models learn to spot the complex, almost invisible patterns that scream "fraud."
For instance, an algorithm might learn that a new login from an unfamiliar city, combined with a first-time purchase at an online store and a checkout process that’s a little too quick, has a high probability of being an account takeover. A traditional rules-based system would almost certainly miss that. Each of those events on its own isn't a huge red flag.
It’s this ability to connect seemingly unrelated dots that gives AI-powered fraud detection in fintech its predictive power. The system isn't just reacting to yesterday's threats; it’s spotting new tricks as they happen, stopping criminals in their tracks before they can do real damage. With that foundation, we can start to look at the specific types of AI models that make all this possible.
Choosing the Right AI Models for Your Business
Picking the right tool for the job is always critical, and in the world of AI-powered fraud detection, that means choosing the right machine learning models. Not all AI is created equal; different models have unique strengths that are better suited for specific types of threats. The choices you make here will define just how effectively your system can learn, adapt, and ultimately protect your business from financial crime.
You’ll mainly come across two categories: supervised and unsupervised learning. The easiest way to think of them is as two different kinds of detectives, each with a specialised method for cracking a case. Understanding how both work is the key to building a truly robust, layered defence.
Supervised Learning: The Seasoned Detective
Supervised learning models are a bit like seasoned detectives who have spent years studying case files of past crimes. They are trained on huge volumes of historical data that have been carefully labelled as either "fraudulent" or "legitimate." This process teaches the model to recognise the tell-tale signs and patterns linked to known fraud tactics.
When a new transaction comes in, the model scrutinises it, comparing its characteristics to the patterns it learned from all that historical data. Based on that comparison, it makes a highly informed prediction on whether the transaction is likely to be a problem.
Two of the most popular and effective supervised models in fintech are:
Random Forests: Imagine you're tackling a complex case and you decide to consult a large, diverse panel of expert investigators. Each one reviews the evidence independently and gives you their verdict. A Random Forest model does something similar; it builds hundreds or even thousands of individual "decision trees" and then pools their outputs to reach a final, highly accurate decision. This collective judgment makes it incredibly resilient and less likely to be swayed by a single flawed perspective.
Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM): This model takes a more collaborative approach. Think of it like building a team of detectives where each new hire is brought on specifically to correct the mistakes made by the previous one. The model builds a sequence of simple decision trees, where each new tree focuses on fixing the errors of the one before it. This iterative process creates a powerful, fine-tuned system that gets exceptionally good at spotting even the most subtle fraud patterns.
Unsupervised Learning: The New-Threat Specialist
Supervised models are fantastic at catching threats we already know about, but what about the new, creative tactics that fraudsters are constantly dreaming up? This is where unsupervised learning really shines. These models are like forward-thinking detectives tasked with finding threats nobody has even seen before.
Instead of being trained on labelled data, unsupervised models sift through your entire dataset to understand its underlying structure and pinpoint outliers – data points that just don't fit the normal pattern. This makes them exceptionally good at spotting novel and emerging fraud schemes before they become widespread problems.
This flowchart illustrates the core decision an AI model makes when flagging an event for potential fraud.
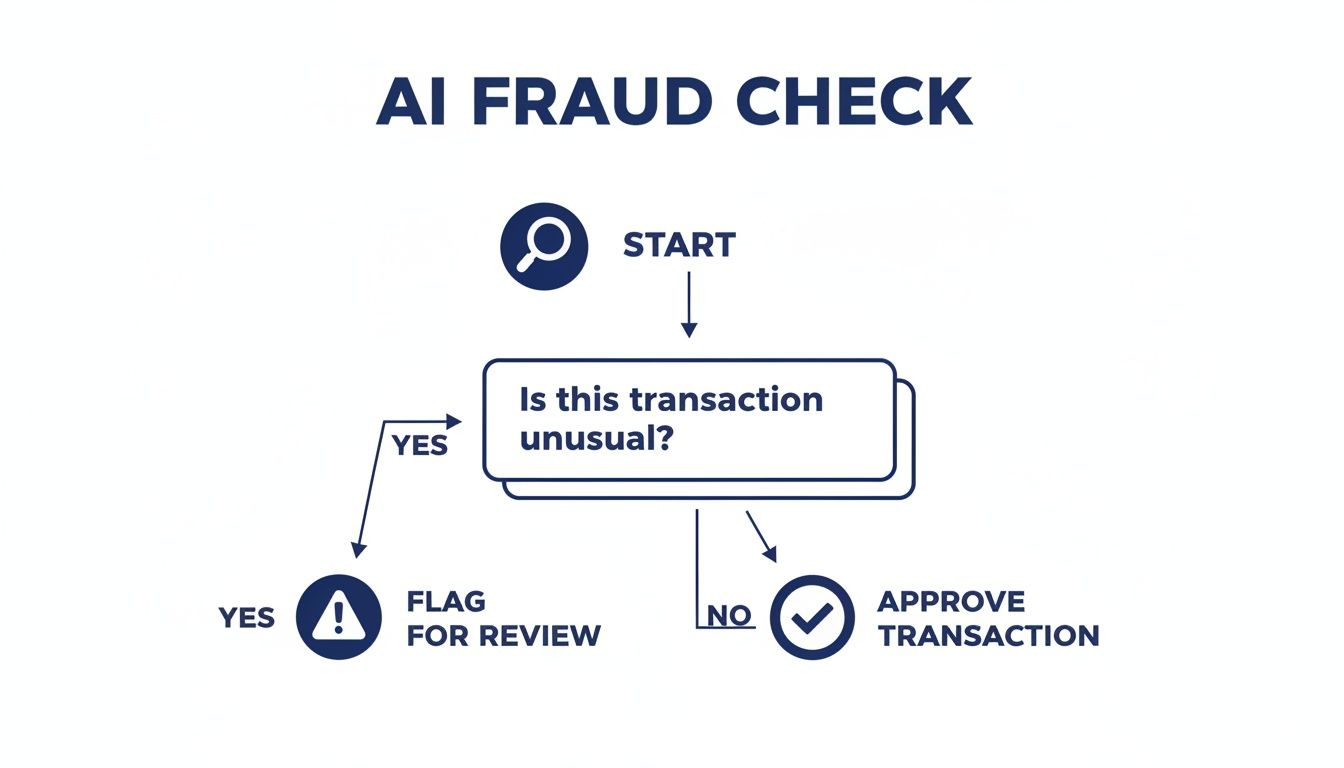
At its heart, the process boils down to identifying unusual behaviour that deviates from an established norm – a key strength of unsupervised learning.
A couple of go-to unsupervised models include:
Isolation Forests: This model cleverly works by trying to "isolate" individual data points. Normal transactions are numerous and tend to be clustered together, making them hard to separate from the pack. Fraudulent transactions, on the other hand, are rare and unusual, making them much easier to single out. It’s like trying to find a single red marble in a giant jar of blue ones; it stands out immediately.
Clustering (e.g., K-Means): This technique groups similar data points together into "clusters." The model can then identify small, isolated clusters of suspicious activities that behave differently from the large clusters of legitimate customer transactions. For instance, it might find a small group of new accounts all opened from the same device, making tiny test purchases right before attempting a large-scale attack.
Comparing AI Models for Fraud Detection
To make the choice clearer, this table breaks down the most common models used in fintech, highlighting where each one excels and what to watch out for.
| AI Model | Best For | Key Strength | Potential Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forests | General-purpose fraud classification; good with complex datasets. | High accuracy and resistant to overfitting. Handles missing data well. | Can be a "black box," making it hard to interpret why a decision was made. |
| Gradient Boosting | Identifying subtle, complex patterns in transaction data. | Often achieves best-in-class performance. Highly accurate. | Slower to train and can be sensitive to noisy data if not tuned properly. |
| Isolation Forests | Detecting new and unknown fraud types (anomaly detection). | Very fast and efficient, especially with large datasets. | Less effective if fraudulent behaviour closely mimics normal patterns. |
| Clustering (K-Means) | Segmenting users to find suspicious groups (e.g., bot networks). | Great for discovering hidden structures and relationships in the data. | Requires specifying the number of clusters beforehand, which can be tricky. |
Choosing the right model is a balance. While a high-performance model like a GBM might seem ideal, a simpler Random Forest could be better if you need more interpretability.
By combining both supervised and unsupervised learning, a fintech company can create a powerful, dual-layered defence. The supervised models act as a strong frontline against known attacks, while the unsupervised models serve as a vigilant watchtower, scanning the horizon for brand-new threats.
Ultimately, the most effective strategy often involves a hybrid system. This ensures you can stop the fraud you know about while also being prepared for the threats you haven’t seen yet. To see how these models fit into a bigger picture, you can explore the broader applications of AI in financial services.
A Practical Roadmap to Building Your AI Defence System
Jumping into an AI-powered fraud detection in fintech project can feel overwhelming, especially for a growing business. But it doesn't have to be a massive, all-or-nothing effort. By breaking it down into manageable phases, even a small team can build a powerful defence system, piece by piece.
The secret is to start small. Zero in on one specific problem, prove the value, and build from there. You don’t need a huge data science department or a blank cheque to start making a real dent in your fraud rates.
Phase 1: Laying the Foundation
Before you even think about code, the first step is to get your bearings. You need to clearly define what "winning" looks like. Pick one specific type of fraud to tackle first: is it account takeovers, payment fraud, or those tricky synthetic identities? Trying to solve everything at once is a recipe for disaster.
With your target locked in, it's time to gather your raw materials: the data. This is, without a doubt, the most critical part of the entire process. Your AI model is only as good as the information you feed it.
Gather Your Data: Pull together historical transaction logs, user info (like demographics, device IDs, and IP addresses), and behavioural data (login times, session lengths). Most importantly, you need clear examples of both legitimate transactions and known fraudulent ones.
Clean and Prepare: Raw data is almost always a mess. You'll need to hunt down and remove duplicate entries, figure out how to handle missing values, and standardise formats. Think of it as a detective meticulously organising all the evidence before even starting to connect the dots.
Feature Engineering: This is where the magic really starts. You'll turn raw data points into meaningful signals or "features" that the AI can understand. For instance, you could create features like ‘number of transactions in the last hour’ or ‘distance between the transaction location and the user’s billing address.’
Phase 2: Model Development and Training
Once you have a clean, feature-rich dataset, you can dive into the fun part: building and training your fraud detection model. A great starting point is often a simpler, more transparent model like a Random Forest. This helps you establish a performance baseline and, crucially, understand why it's making certain decisions.
During this phase, you'll split your data into three distinct piles:
Training Set: This is the biggest chunk, used to teach the model how to spot the patterns of fraud.
Validation Set: This set is used to fine-tune the model's settings and make sure it's learning correctly.
Testing Set: Kept completely separate and unseen by the model, this data is used for a final, unbiased exam to see how it performs in the real world.
This loop of training, validating, and testing is absolutely essential. It’s like putting a rookie detective through training, quizzing them on old case files, and then sending them to a new crime scene to see if they can solve it on their own.
Phase 3: Evaluation and Understanding Performance
After your model is trained, you need to measure how good it actually is. When it comes to fraud detection, two metrics really matter:
Precision: Out of all the transactions your model flagged as fraud, how many were really fraudulent? High precision means you're not falsely accusing and inconveniencing legitimate customers.
Recall: Of all the actual fraudulent transactions that happened, how many did your model catch? High recall means fewer fraudsters slip through the net.
There's almost always a tug-of-war between these two. If you tune the system to be overly aggressive, you'll get high recall but low precision (too many false alarms). If it's too cautious, you'll have great precision but low recall (you'll miss a lot of fraud). The goal is to find that sweet spot that protects your business without creating a nightmare for your customers.
Phase 4: Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
Putting your model into production means plugging it into your live transaction flow. A safe way to start is by running it in "shadow mode." Here, it analyses transactions and makes predictions in the background without actually blocking anything. This lets you see how it behaves with live data, risk-free.
Once you’re confident in its accuracy, you can flip the switch and let it actively flag or block suspicious activity. But the job isn't done. Fraudsters are always evolving their tactics, which means your model can't afford to stand still. You need to regularly retrain it with new data to keep it sharp and effective against the latest threats.
This ongoing commitment is vital. The Canadian generative AI in fintech market, currently valued at $2.5 billion, is expected to skyrocket to $12.5 billion by 2035, with fraud detection as a major driver. This incredible growth underscores the need for smart, adaptive defences.
Navigating Canadian Compliance and Data Privacy

So, you’ve built a sharp, effective AI fraud detection system. That's the hard part, right? Not quite. Getting the technology right is only half the battle; making sure it plays by Canada's rules is where the real work often begins.
In Canada, fintech doesn’t operate in a Wild West environment. We have a solid regulatory framework designed to protect consumers, and your AI system has to live and breathe within those rules. Ignoring them isn't just a slap on the wrist; it can lead to massive fines, a complete loss of customer trust, and even halt your operations.
The Key Players in Canadian Regulation
To get this right, you first need to know who’s watching. In Canada, three main bodies set the guidelines that will directly shape how you build and run your AI models.
OSFI (Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions): Think of OSFI as the guardian of stability for banks and insurance companies. If you're providing services to any federally regulated institution, their guidelines on technology and cyber risk are your bible.
FINTRAC (Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada): This is Canada's financial intelligence unit, laser-focused on stopping money laundering and terrorist financing. Your AI models need to be sharp enough to flag suspicious activity in a way that aligns with FINTRAC's strict reporting standards.
FCAC (Financial Consumer Agency of Canada): The FCAC is all about fairness. They make sure financial services are transparent and don't harm the consumer. For your AI, this means proving it isn't making biased or discriminatory decisions that unfairly penalise certain customers.
These agencies are keeping a close eye on a booming industry. Canada's AI in fintech market was already worth USD 923.2 million back in 2022 and is expected to rocket to USD 2,896.2 million by 2030, with fraud detection leading the charge. You can read the full research about Canada's AI in fintech market to get a sense of the scale.
Data Privacy and the Black Box Problem
Beyond the big institutional rules, there's the critical matter of personal data. Canada's Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) dictates exactly how you can collect, use, and store personal information. When you're feeding data into an AI model, you have to be absolutely sure your practices are compliant, from getting clear consent to being upfront about what you're doing with it.
This brings us to one of AI’s trickiest hurdles: the "black box" problem. The most powerful models can be incredibly accurate, but they often can't tell you why they flagged a specific transaction as fraudulent.
For an auditor or a regulator, a shrug and "the AI just said so" is the worst possible answer. They demand explainability and transparency. You have to be able to pull back the curtain and show that your model's decisions are fair, logical, and free of bias.
This is precisely why your choice of models and documentation from day one is so crucial. By investing in explainable AI (XAI) techniques, you give yourself the tools to peek inside that black box and defend your system’s logic. Building a compliant system is a foundational step in the broader journey of technology adoption, as many businesses are discovering. For more on that, you might find our guide on AI adoption in Canadian enterprises helpful.
Seeing AI Fraud Detection in Action
Theory and roadmaps are one thing, but the true measure of any technology is what it can do in the real world. Let’s move beyond the abstract and look at a few examples of how AI-powered fraud detection in fintech helps companies turn a serious vulnerability into a real strength.
These mini case studies show how different businesses tackled unique fraud challenges with specific AI strategies. It’s proof that this technology isn't just for the big players; it's accessible and effective for organisations of all sizes. Each story breaks down a common problem, the AI solution used to fix it, and the results they could actually measure.
Slashing Chargebacks for an E-commerce Startup
An up-and-coming online retailer was getting hammered by chargeback fraud. Crooks were using stolen credit card numbers for purchases, and the resulting chargeback fees were wiping out their already thin profit margins. Their old, rule-based system was completely outmatched, and they were starting to get a bad reputation with their payment processors.
The Solution:
They brought in a hybrid AI model, mixing supervised and unsupervised learning to get the best of both worlds.
Supervised Learning: First, they trained a Random Forest model on all their past transaction data. This taught the AI to spot well-known fraud patterns, like when a billing address is in one country, and the shipping address is in another, or when an order is unusually large.
Unsupervised Learning: Next, they used an Isolation Forest to watch user behaviour in real-time. This model was great at flagging strange activity that didn't fit a known pattern, like someone flying through the checkout process suspiciously fast or placing multiple orders from the same IP address with different credit cards.
The Outcome:
The results were impressive. Within six months, the startup saw a 40% reduction in chargeback fraud. This didn't just save them money; it rebuilt their trust with payment providers, which helped them negotiate better processing rates down the line.
Uncovering Hidden Fraud in Insurance Claims
A mid-sized insurance provider had a growing suspicion that they were being targeted by organised fraud rings. The criminals were submitting claims with tiny alterations that were almost impossible for a human adjuster to catch one by one. The financial bleed was adding up fast, costing them hundreds of thousands of dollars every year.
The real challenge was connecting the dots between claims that looked completely unrelated on the surface. A single fraudulent claim might seem perfectly fine, but the AI was able to see the bigger picture – a coordinated attack in progress.
The Solution:
The company adopted a strategy based on behavioural analytics and network analysis. Their new AI system started by learning what normal claimant behaviour looked like and then flagged anyone who deviated from that baseline. More importantly, it started mapping the relationships between claimants, doctors, and repair shops to uncover suspicious clusters.
The Outcome:
It didn’t take long for the AI to flag a whole network of claimants who were all using the same handful of medical providers and lawyers. That tip-off sparked an investigation that exposed a massive fraud ring, saving the company an estimated $750,000 in the first year alone. Beyond just catching fraudsters, AI is finding practical uses all over fintech security, including specialised AI-assisted debugger solutions that help teams quickly find and fix complex system problems.
Securing Loans at a Local Automotive Dealership
A local car dealership offered online financing and was getting burned by synthetic identity fraud. Fraudsters were piecing together fake identities using a mix of real and fabricated information – just enough to scrape by a basic credit check. They’d secure a loan, drive off with a car, and never make a single payment.
The Solution:
The dealership put an AI-powered identity verification system in place. This tool was designed to analyse application data for the subtle red flags that point to a synthetic identity. It could cross-reference details across different databases and flag applications with high-risk signals, like a brand-new email address paired with a very thin credit file.
The Outcome:
The new system slammed the door on this type of loan fraud. By catching these bogus applications before they were ever approved, the dealership prevented over $200,000 in potential losses in just its first three months of operation.
Got Questions About AI Fraud Detection? We've Got Answers
Stepping into the world of AI can feel like navigating new territory. It’s only natural to have questions. Here are some of the most common ones we hear from business leaders and tech teams, with straight-talking answers to help you see the path forward.
How Much Data Do We Really Need to Get Started?
You might be surprised to learn you don't need a mountain of data. For most businesses, your existing transaction history from the past one to two years is more than enough to get the ball rolling.
The secret isn't a massive volume of data; it's the quality. A clean, well-labelled dataset, even with just a few hundred thousand transactions, can be the foundation for a very effective first model. What truly matters is having clear examples of both good and bad transactions for the AI to learn from.
And if you're a newer company without a deep history? No problem. That's a perfect scenario for unsupervised models, which are brilliant at spotting unusual activity without needing historical fraud labels.
Will We End Up Blocking Good Customers by Mistake?
That’s a big concern, and rightly so. Annoying your legitimate customers is the last thing anyone wants. This is precisely where modern AI systems shine and leave old, rigid rule-based engines in the dust.
AI models are much smarter than a simple checklist of rules. They understand context. An AI can tell the difference between you buying souvenirs on holiday and a thief trying to drain your account from a strange location. It’s all about nuance.
Plus, you can set up smarter responses. Instead of a hard block, a slightly fishy transaction might just trigger a quick two-factor authentication request. It’s about being firm with fraudsters but flexible with your real customers.
The real magic of AI is finding that perfect balance: making life seamless and secure for your good customers while putting up a brick wall against the bad guys. It protects your bottom line without ruining the customer experience.
Is an AI Solution Actually Affordable for a Small Business?
Yes, it absolutely is. The days when AI was reserved for mega-corporations with huge data science teams are long gone. Today, many of the best tools are available as "as-a-service" (SaaS) platforms. This means you can get started with a manageable subscription fee that scales with your needs.
When you're looking at the price tag, remember to weigh it against the true cost of doing nothing. Fraud isn't just about the direct financial hit. It's about the damage to your reputation and the loss of customer trust, which can cost you far more in the long run.
Ready to build a resilient, intelligent defence against fraud? Cleffex Digital Ltd specialises in creating custom AI solutions that protect your business and help you grow securely. Discover how we can help.







